Every morning, millions of people worldwide start their day on the wrong foot—quite literally. Imagine waking up to a sharp, stabbing pain in your heel, turning those first few steps out of bed into a wince-inducing ordeal. This isn’t just a bad start to the day; for those with Plantar Fasciitis, it’s a recurrent reality that deeply impacts their daily lives. A staggering statistic reveals that 1 in 10 individuals will encounter this debilitating foot condition at some point, underscoring its prevalence and the widespread need for effective management strategies.
Plantar Fasciitis doesn’t just steal the joy from mornings; it transforms simple activities—walking, running, or even standing into a kitchen counter—into daunting, often painful tasks. The condition extends its influence beyond physical discomfort, affecting personal well-being, work productivity, and overall quality of life. For some, it means giving up cherished morning jogs or evening walks. For others, it’s a constant search for shoes that might offer just a bit more comfort.
Beyond its personal toll, Plantar Fasciitis carries significant economic implications, contributing to millions in healthcare expenditures each year. These costs stem from treatments, lost workdays, and ongoing management of the condition, highlighting the urgent need for effective prevention and treatment approaches.
Chapter 1: The Basics of Plantar Fasciitis
Understanding the Condition
Imagine the arch of your foot as a bow—the kind used in archery. The bowstring that supports this arch stretching from your heel to the front of your foot, resembles the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue. Plantar Fasciitis occurs when this “bowstring” becomes inflamed, akin to an overused or frayed string on a bow, leading to pain at the heel or along the arch of the foot. This condition is most notorious for causing significant discomfort during the first steps after waking up or after long periods of rest.
To help visualize this, imagine a simple diagram: the foot’s outline with a highlighted arch representing the plantar fascia. An arrow could indicate the direction of stress or inflammation, helping to illustrate how pressure on this area can lead to pain.
Demystifying the Causes
The causes of Plantar Fasciitis are as varied as the people it affects, but they often boil down to undue stress and strain on the plantar fascia. Let’s explore some of the primary culprits and offer tips for prevention along the way:
Excessive Running or Walking: Especially on hard surfaces, can accelerate wear and tear on the plantar fascia. The repetitive impact significantly strains this crucial ligament, increasing the risk of inflammation and pain.
Preventive Tips:
- Incorporate Low-Impact Exercises: To give your feet a break from the constant pressure, consider adding low-impact activities to your exercise routine. Swimming and cycling are excellent alternatives that allow you to maintain cardiovascular fitness without putting excessive stress on your plantar fascia.
- Strengthen the Plantar Fascia and Related Muscles: Regular exercises aimed at strengthening the plantar fascia, along with the muscles of the foot and lower leg, can improve the foot’s ability to handle the load during activities like walking and running. Strengthening these areas helps disperse the stress more evenly, reducing the likelihood of pain. Exercises such as toe curls, arch lifts, and calf raises can be particularly beneficial. By enhancing the strength and flexibility of the foot’s supporting structures, you can minimize the risk of Plantar Fasciitis and enjoy a reduction in discomfort from existing conditions.
Improper Footwear: Shoes that lack proper support or cushioning can contribute significantly to the problem. Preventive Tip: Invest in shoes with good arch support and replace them regularly. Consider orthotic inserts for additional support.
Obesity or Sudden Weight Gain: Extra pounds can put additional stress on your plantar fascia. Preventive Tip: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can alleviate some of the pressure on your feet.
Tight Achilles Tendons or Calf Muscles: These conditions can pull on the heel and aggravate the plantar fascia. Preventive Tip: Regularly stretch your calves and Achilles tendon to increase flexibility and reduce tension on the plantar fascia.
Standing for Long Periods: Jobs or activities that require long hours on your feet can increase the risk of Plantar Fasciitis. Preventive Tip: Take frequent breaks to sit down, and when standing, try to alternate your weight or move around to different positions.
Understanding the causes of Plantar Fasciitis is the first step toward prevention and treatment. By addressing these factors proactively, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this painful condition, ensuring that their feet remain strong and healthy for years to come.
Chapter 2: Who’s at Risk?
Understanding who is more likely to develop Plantar Fasciitis helps in both prevention and early identification of the condition. While this foot ailment can affect virtually anyone, certain factors increase the likelihood of experiencing its unwelcome symptoms.
Identifying Risk Factors
Several demographics and lifestyles stand out when considering the risk of developing Plantar Fasciitis:
- Age: Individuals between the ages of 40 and 60 are more commonly affected. This age group often experiences changes in body weight, activity levels, and tissue elasticity, contributing to the risk.
- Runners and Athletes: The repetitive impact on the feet during activities like long-distance running, ballet dancing, and aerobic exercise puts athletes at a higher risk.
- Occupational Hazards: People who spend most of their day standing or walking on hard surfaces—such as teachers, factory workers, and healthcare professionals—are more susceptible due to the constant pressure on their plantar fascia.
- Foot Mechanics: Flat feet, a high arch, or even an abnormal walking pattern can distribute weight unevenly across the foot, increasing the strain on the plantar fascia.
- Obesity: Excess body weight significantly increases the stress on the plantar fascia, making obesity a prominent risk factor for Plantar Fasciitis.
Lifestyle and Plantar Fasciitis: How Daily Habits Contribute to Risk
Our daily habits and choices play a significant role in either increasing or decreasing our risk of developing Plantar Fasciitis. Here’s how lifestyle impacts this risk and what changes can mitigate it:
- Physical Activity Levels: Regular, moderate exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and strengthens the muscles supporting the arch of the foot, reducing stress on the plantar fascia. Conversely, sudden increases in activity levels can spike the risk.
- Footwear Choices: Frequently wearing high heels or shoes with inadequate support can strain the plantar fascia. Opting for well-fitted, supportive shoes can drastically reduce risk.
- Weight Management: Since obesity is a significant risk factor, adopting a balanced diet and maintaining an active lifestyle are crucial preventive measures.
- Workplace Ergonomics: For those in standing occupations, using anti-fatigue mats and taking regular breaks to sit or stretch can alleviate prolonged pressure on the feet.
- Stretching and Flexibility: Incorporating daily stretches for the calf muscles and the plantar fascia itself can enhance flexibility, significantly reducing the risk of inflammation.
By identifying and modifying risk factors within our control, individuals can greatly diminish their chances of encountering Plantar Fasciitis. This proactive approach empowers people to safeguard their foot health and enhance their overall well-being.
Chapter 3: Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis
Understanding the pathway to diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis can demystify the process and ease anxieties about seeking professional help. This chapter aims to walk you through what typically happens during the diagnosis phase, highlighting the non-invasive nature of most evaluations.
The Path to Diagnosis
The journey to diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis often begins with recognizing the hallmark symptom: a sharp, stabbing pain in the bottom of your foot, especially with the first steps in the morning or after periods of rest. Once you decide to seek medical advice, here’s what you can generally expect:
- Medical History Review: Your healthcare provider will start by discussing your symptoms and medical history. This conversation is crucial for understanding the context of your foot pain, including when it started, any activities that exacerbate or alleviate it, and whether you have any underlying health conditions that might contribute to it.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will examine your foot, looking for areas of tenderness. The location of your pain can help confirm whether you have Plantar Fasciitis. They’ll also assess the arch of your foot, checking for flat feet or high arches, and may evaluate your walking pattern to identify any abnormalities.
What to Expect at Your Appointment
Being prepared for your appointment can help you make the most of your time with the healthcare provider. Here’s what to expect and how to prepare:
- Potential Questions: Be ready to answer questions about the nature of your foot pain (e.g., “Does the pain improve as the day goes on?” or “What activities exacerbate your symptoms?”). Also, think about any recent changes in your activity level, footwear, or lifestyle that could be relevant.
- Physical Tests: While most diagnoses are based on history and physical examination, your doctor might perform specific tests to rule out other conditions. These can include flexing your foot to stretch the plantar fascia, which can trigger symptoms if Plantar Fasciitis is present.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, if the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out other causes of heel pain, your healthcare provider might order imaging tests. These could include X-rays to rule out bone fractures or bone spurs or an ultrasound to visualize the plantar fascia in detail. Rest assured, these tests are non-invasive and painless.
Understanding that the diagnostic process for Plantar Fasciitis is straightforward and primarily non-invasive can alleviate concerns about seeking medical evaluation. Being well-informed about your condition and the diagnostic steps can also empower you to play an active role in your treatment plan, setting the stage for a successful recovery.
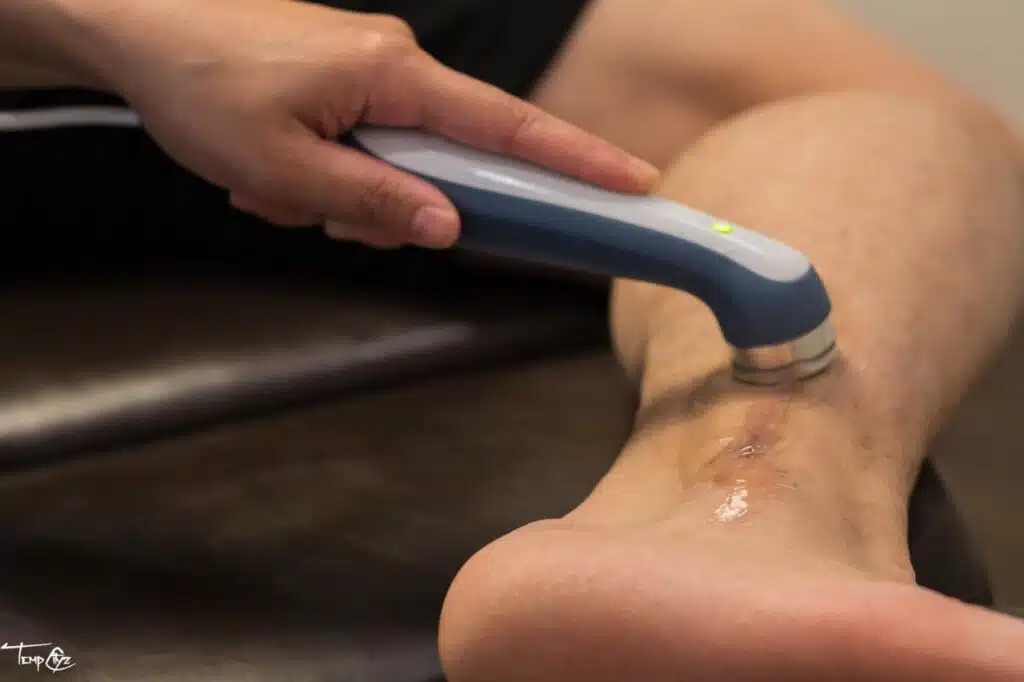
Chapter 4: Treatment Strategies
Successfully managing Plantar Fasciitis involves a combination of immediate relief measures for acute pain and long-term strategies to address the underlying causes. This comprehensive approach helps ensure not just temporary relief but a lasting solution to the pain and discomfort associated with this condition.
Immediate Relief Measures
For those moments when the pain flares up, several home remedies and self-care measures can offer quick relief:
- Ice Therapy: Applying an ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Ensure you wrap the ice pack in a cloth to protect your skin.
- Rest and Elevation: Minimizing activities that exacerbate the pain, especially those that involve prolonged standing or walking, can be beneficial. When resting, elevating the foot can help reduce swelling.
- Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon, plantar fascia, and calf muscles can relieve tension and pain. These exercises are best done in the morning before taking your first steps and throughout the day as needed.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Long-term Treatment Options
A more strategic, long-term approach to managing Plantar Fasciitis is necessary for sustained relief and to prevent recurrence. This includes a combination of physiotherapy, orthotic support, and, in some cases, more advanced treatments like shockwave therapy or surgery.
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the foot and ankle, improving stability and support for the plantar fascia.
- Orthotics: Custom-fitted arch supports or orthotic inserts can distribute pressure more evenly across your foot, alleviating stress on the plantar fascia. Over-the-counter options are available, but custom orthotics prescribed by a professional are preferred for the best fit and effectiveness.
- Shockwave Therapy: Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment for Plantar Fasciitis, particularly for chronic cases resistant to traditional therapies. This therapy uses sound waves to stimulate healing within the plantar fascia, promoting the repair of damaged tissue and reducing pain. Studies have shown that shockwave therapy can be effective in reducing symptoms for patients with persistent Plantar Fasciitis, making it a viable option before considering surgical interventions.
- Surgery: Surgery is considered only in cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide relief after several months. The most common procedure involves releasing part of the plantar fascia from the heel bone to reduce tension. However, surgery is a last resort due to the potential for complications and the lengthy recovery time.
Exploring Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care is an alternative treatment option that has shown promise for some individuals with Plantar Fasciitis. Chiropractors focus on the body’s musculoskeletal alignment, and adjustments can:
- Improve Foot Mechanics: Adjustments can help correct structural misalignments in the feet, potentially reducing the strain on the plantar fascia.
- Enhance Mobility: Chiropractic care may increase joint mobility in the foot and ankle, improving function and aiding in the recovery process.
- Alleviate Pain: Some patients report immediate relief from pain following chiropractic adjustments, though individual experiences may vary.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your situation. Whether through immediate relief measures, long-term strategies, or exploring other treatments like chiropractic care, managing Plantar Fasciitis effectively requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s needs and lifestyle.
Chapter 5: Preventing Plantar Fasciitis
Prevention is key to avoiding the onset or recurrence of Plantar Fasciitis. Incorporating simple, daily practices into your routine can significantly reduce your risk. This chapter provides strategies recommended by health professionals for maintaining foot health and preventing Plantar Fasciitis.
Daily Practices for Prevention
Adopting the following habits can help keep your feet healthy and free from pain:
- Wear Supportive Footwear: Choose shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel to reduce stress on your plantar fascia. Avoid walking barefoot on hard surfaces, which can increase the strain on your feet.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight puts additional pressure on your plantar fascia. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and regular exercise can alleviate this strain.
- Gradually Increase Activity Levels: Whether you’re taking up a new exercise routine or increasing your daily activity, do so gradually. Sudden increases in activity can shock the plantar fascia and lead to inflammation.
- Alternate Your Activities: Mix up your exercise routine to avoid repetitive stress on your feet. Incorporating low-impact activities like cycling or swimming can give your plantar fascia a rest.
- Stretch Regularly: Daily stretches targeting the Achilles tendon, calf muscles, and plantar fascia can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Exercise and Foot Health
Specific exercises can strengthen the foot and improve flexibility, further reducing the risk of Plantar Fasciitis. Here are some exercises recommended by health professionals:
- Towel Curls: Place a towel flat on the floor and use your toes to scrunch it towards you, then push it away. This exercise helps strengthen the muscles of the foot and arch.
- Toe Stretches: Sit with your legs extended in front of you. Use a towel looped around your foot to gently pull your toes back towards you. Hold for 15-30 seconds to stretch the plantar fascia.
- Calf Raises: Stand on the edge of a step with your heels hanging off. Slowly raise your heels as high as possible, then lower them below the level of the step. This exercise strengthens the muscles around the ankle and improves flexibility in the Achilles tendon.
- Achilles Tendon Stretch: Place your hands on a wall and step one foot back, keeping it straight. Bend your front knee and lean forward, keeping your back heel on the ground. Hold for 15-30 seconds to stretch the Achilles tendon and calf muscles.
Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can significantly improve the strength and flexibility of your feet, reducing the risk of developing Plantar Fasciitis. Remember, consistency is key to prevention. By taking proactive steps each day, you can maintain healthy feet and avoid the discomfort associated with this condition.
Conclusion
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential facets of Plantar Fasciitis, from understanding the condition and identifying who’s at risk to diagnosing, treating, and, most importantly, preventing it. The journey through each chapter has equipped you with the knowledge to not only confront Plantar Fasciitis head-on but also to take proactive steps toward maintaining foot health and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Plantar Fasciitis is crucial for recognizing symptoms early on. Remember, it’s not just about the morning pain; it’s about acknowledging when something doesn’t feel right in your feet.
- Identifying Risk Factors helps in assessing your likelihood of developing Plantar Fasciitis. Awareness of these factors empowers you to make informed decisions about your lifestyle and activities.
- Early Diagnosis is essential for effective management. The sooner you address the symptoms, the better your chances of avoiding prolonged discomfort.
- Treatment Strategies should be multifaceted, combining immediate relief measures with long-term solutions to ensure both acute and enduring relief.
- Prevention is key. Adopting daily practices and exercises designed to strengthen and protect your feet can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence.
Addressing symptoms early cannot be overstated. Plantar Fasciitis, while common, is not a condition to be ignored or taken lightly. The impact of untreated foot pain can extend far beyond the physical discomfort, affecting your mobility, lifestyle, and even mental health. The pain is not just a signal but a call to action—a reminder that your body needs attention and care.
Do not ignore foot pain. If you suspect you’re dealing with Plantar Fasciitis or if you’re experiencing persistent pain in your feet, seeking professional advice promptly can make a significant difference in your recovery journey. Healthcare professionals can provide you with a tailored approach, ensuring you receive the most effective treatment for your specific situation.
Remember, taking care of your feet is not just about avoiding pain; it’s about embracing an active, healthy lifestyle free from limitations. With the right knowledge, practices, and care, you can step forward confidently, knowing you’re doing your best for your foot health.
Additional Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into Plantar Fasciitis management, enhance their understanding of foot health, or find support, the following resources can be invaluable. Whether you’re seeking the latest research, advice from experts, or a community of individuals sharing similar experiences, a wealth of information and support is available.
- Canadian Podiatric Medical Association (CPMA): A comprehensive source for finding licensed podiatrists across Canada and accessing a range of educational materials on foot health, including Plantar Fasciitis. https://www.podiatrycanada.org
- Canadian Orthopedic Foundation: Offers resources and information on various conditions, including foot health. Their website includes patient stories, treatment options, and a directory to find orthopedic surgeons in Canada. http://www.canorth.org
- Canadian Physiotherapy Association: Provides information on how physiotherapy can help with foot conditions like Plantar Fasciitis. The site also includes a tool to find a physiotherapist near you. https://physiotherapy.ca
- HealthLink BC: Offers comprehensive health information and advice, including self-care for Plantar Fasciitis, directly from the British Columbia Ministry of Health. This resource is particularly useful for understanding treatment options available within the Canadian healthcare system. https://www.healthlinkbc.ca
- MyHealth.Alberta.ca: A government of Alberta resource offering detailed guides on various health conditions, including Plantar Fasciitis. It provides symptom descriptions, management tips, and when to seek medical attention. https://myhealth.alberta.ca
- Canadian Diabetes Association: Since individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk for foot problems, including Plantar Fasciitis, this association offers resources and tips for foot care to prevent complications. https://diabetes.ca
- Arthritis Society Canada: Plantar Fasciitis can be related to arthritis in some cases. This society offers resources and support for managing arthritis-related foot pain. https://arthritis.ca
Remember, these resources are meant to complement professional medical advice. For specific concerns or symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your health needs.






0 Comments