Knee pain is a common complaint that affects individuals of all ages, often significantly impacting their quality of life. Whether it stems from an injury, a chronic condition, or the wear and tear of daily life, the implications of knee pain can be far-reaching, affecting mobility, independence, and overall well-being. The knee, being a critical joint in the human body, plays a vital role in our ability to move, support weight, and engage in a range of activities. Understanding the complexities of knee pain is not just important – it’s essential for effective management and treatment.
In Canada, knee pain is one of the leading causes of physical discomfort and disability, prompting a significant number of medical consultations each year. This prevalence underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of knee pain – from its causes and symptoms to the most advanced diagnostic methods and treatment options available. With an ever-growing array of medical advancements and therapeutic approaches, staying informed is key to effective knee pain management.
This guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of knee pain, covering its various aspects in detail. We’ll delve into the anatomy and function of the knee, examine common injuries and diseases affecting this crucial joint, and discuss the latest diagnostic technologies. Our journey will also take us through a range of treatment modalities, from chiropractic care and physiotherapy to cutting-edge surgical interventions. Additionally, we’ll explore preventive care strategies, emphasizing the importance of maintaining knee health through exercise, lifestyle adjustments, and proper nutrition.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of knee pain, equipping you with the knowledge to manage it effectively and make informed decisions about your health or that of your loved ones. So, let’s begin our journey into the world of knee pain, understanding its intricacies and exploring the many ways we can address this common yet complex ailment.
Anatomy and Function of the Knee
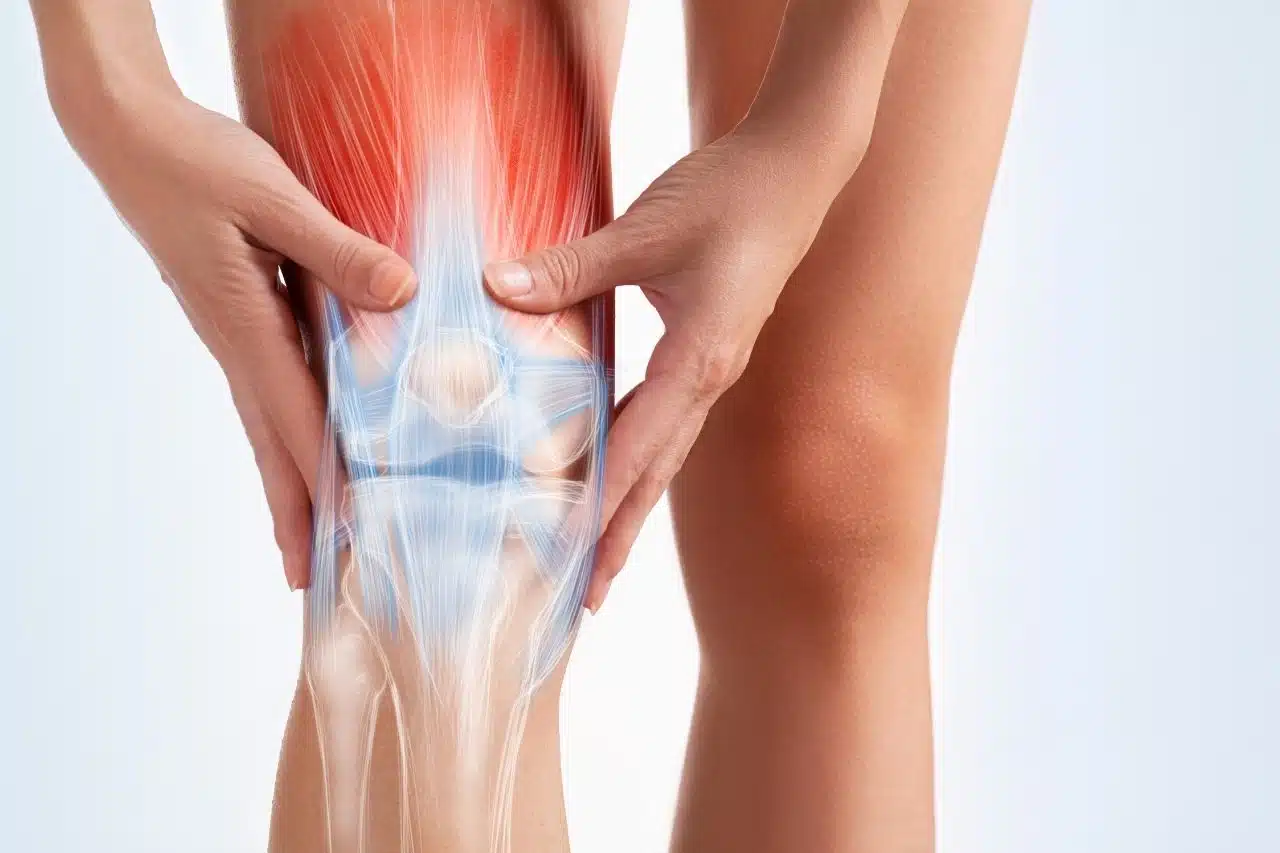
The knee is not just a hinge joint; it’s a complex structure that plays a pivotal role in almost every movement we make. Understanding its anatomy and function is crucial in comprehending the various types of knee pain and their causes.
Detailed Look at Knee Structure
The knee joint is formed where three bones meet: the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). This joint is supported and stabilized by a network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Key structures include:
- Ligaments: Bands like the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) provide stability and control the joint’s movements.
- Cartilage: Menisci, two C-shaped pieces of cartilage, act as shock absorbers, cushioning the joint and helping distribute weight evenly.
- Tendons: The patellar tendon connects the kneecap to the shin bone and is essential for movements like running and jumping.
Importance in Movement and Support
The knee joint is integral to many daily activities, such as walking, sitting, standing up, and climbing stairs. It allows for bending (flexion), straightening (extension), and a small degree of rotation. The joint’s design provides both stability and flexibility, balancing the need to support the body’s weight with the requirement for dynamic movement.
The health of the knee joint is vital not only for athletes and physically active individuals but for everyone. As a weight-bearing joint, the knee is subject to a variety of stresses and strains throughout life. Maintaining the health and functionality of this joint is key to preserving mobility and independence, especially as we age.
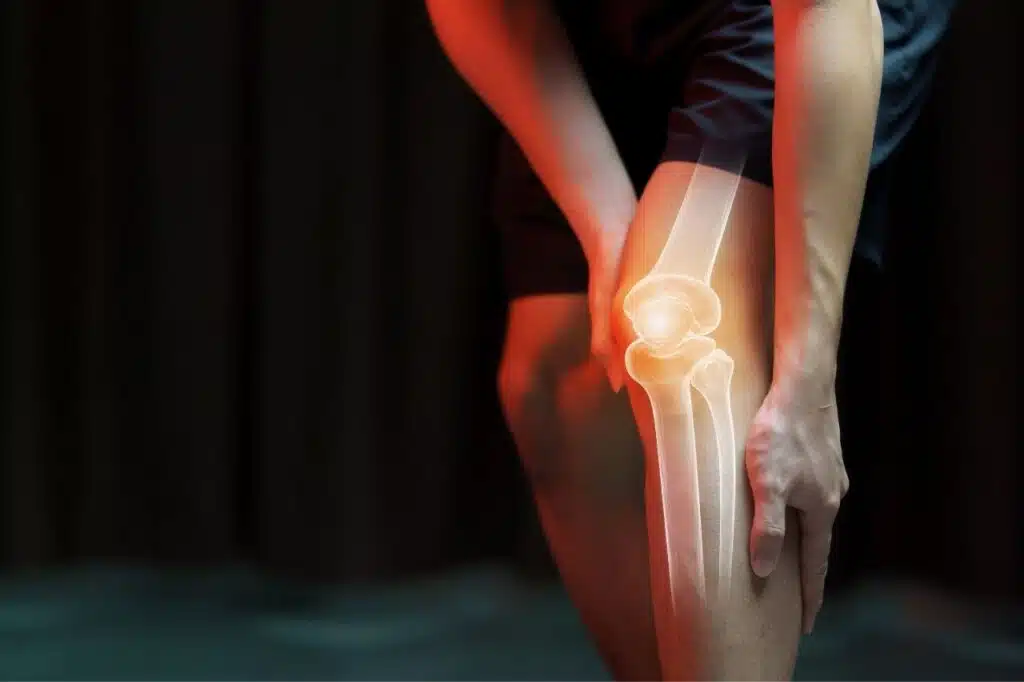
In the following sections, we will explore the common issues that can arise in this complex joint, from acute injuries to chronic conditions. By understanding the intricate workings of the knee, we can better appreciate the challenges involved in diagnosing and treating knee pain.
Common Knee Injuries and Diseases
Knee pain can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from acute injuries to chronic degenerative diseases. Understanding these conditions is key to their diagnosis and management.
In-depth Exploration of Conditions
- ACL Injury: The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments that help stabilize the knee joint. ACL injuries involving sudden stops or direction changes are common in sports. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee.
- Meniscus Tears: The menisci act as shock absorbers in the knee joint. Tears can occur from both acute trauma and degenerative processes. Symptoms often include pain, swelling, and difficulty in knee movement.
- Osteoarthritis: This is a chronic condition characterized by the degeneration of cartilage in the joints. In the knee, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling, often worsening over time.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner’s Knee): This condition is characterized by pain around the kneecap. It’s often seen in athletes but can affect anyone. Causes include overuse, misalignment, and muscle imbalances.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, the small sacs of fluid that cushion the outside of the knee joint, can lead to pain and swelling.
Lesser-Known Knee Ailments
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS): ITBS is an overuse injury commonly seen in runners and cyclists. The iliotibial band, running along the outside of the thigh from the hip to the shin, becomes tight or inflamed, causing pain on the outside of the knee.
- Osgood-Schlatter Disease: Typically affecting adolescents during growth spurts, this condition is characterized by pain and swelling just below the knee.
- Jumper’s Knee (Patellar Tendinitis): This overuse injury involves inflammation of the patellar tendon, leading to pain just below the kneecap, particularly in jumping sports.
These conditions highlight the knee’s susceptibility to a range of injuries and diseases. The next section will discuss the advanced diagnostic methods employed to identify these knee issues accurately.
Advanced Diagnostic Methods
Accurate diagnosis is critical in the effective management of knee pain. Thanks to advancements in medical technology, a variety of sophisticated diagnostic tools are available to healthcare professionals. These methods help not only pinpoint the exact cause of knee pain but also plan appropriate treatment strategies.
Latest Technologies and Imaging Techniques
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is a powerful tool for visualizing the knee’s soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. It is particularly useful in diagnosing soft tissue injuries like ACL tears and meniscal injuries.
- X-rays: Although they cannot show soft tissues like ligaments and tendons, X-rays are effective in revealing bone changes, fractures, and signs of osteoarthritis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans provide a more detailed view than X-rays, which is particularly useful in assessing complex fractures.
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique is used to visualize soft tissue structures around the knee. It can also guide procedures such as injections.
- Arthroscopy: Though more invasive, arthroscopy involves inserting a small camera into the knee joint to visualize the internal structures directly. It’s often used both for diagnosis and treatment.
Role of Different Diagnostic Tools
Each diagnostic tool plays a unique role in knee pain assessment:
- MRI offers a detailed image of the knee’s internal structures, making it invaluable for diagnosing soft tissue injuries.
- X-rays are often the first line of imaging used to rule out fractures and assess for degenerative changes.
- CT scans are particularly useful in complex cases where bone detail is crucial.
- Ultrasound is beneficial for its real-time imaging capability, especially in assessing dynamic knee function and guiding certain treatments.
- Arthroscopy, while more invasive, provides a direct look inside the joint, often confirming diagnoses made with other methods.
The choice of diagnostic method depends on the suspected condition, symptoms, and initial assessment findings. In the next section, we’ll explore the comprehensive treatment approaches for managing knee pain, including both conservative and surgical options.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment of knee pain requires a multifaceted approach, combining various therapeutic techniques and, in some cases, surgical interventions. Treatment choice depends on the underlying cause of the pain, the severity of the condition, and the individual patient’s needs and goals.
Chiropractic and Physical Therapy Techniques
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like joint mobilization can help improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Exercise Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee can enhance stability and reduce the load on the knee joint.
- Therapeutic Modalities: Methods such as ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, shockwave therapy, and cold/heat therapy can aid in pain relief and tissue healing. Shockwave therapy, specifically, is beneficial for promoting healing and pain reduction through the use of focused acoustic waves.
- Gait Analysis and Education: Understanding and correcting walking patterns can be crucial in preventing and treating knee pain, especially in athletes.
Surgical Options and Their Indications
In cases where conservative treatments are insufficient, surgical options may be considered:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Used for a range of conditions, including meniscus tears and ligament repairs. It involves small incisions and the use of a camera to guide the surgery.
- Total Knee Replacement: In severe osteoarthritis or other debilitating joint diseases, replacing the knee joint with an artificial one can significantly improve the quality of life.
- ACL Reconstruction: For ACL tears, surgery often involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft.
Emerging Treatment Methods
- Laser Therapy: This approach uses low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes to alter cellular function, providing pain relief and reducing inflammation. It’s becoming more popular for its non-invasive nature and minimal side effects.
- Aquatic Therapy: Also known as hydrotherapy, this method involves performing exercises in a water environment. The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the knee joint, making it an excellent option for gentle rehabilitation and pain management.
Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual, taking into account the specific diagnosis, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s activity level and overall health.
In the next section, we will delve into preventive care and rehabilitation strategies, highlighting how maintaining knee health can be as important as treating existing conditions.
Preventive Care and Rehabilitation
Maintaining knee health and preventing injuries are as important as treating existing conditions. A well-rounded approach to knee care involves regular exercise, lifestyle modifications, and understanding the importance of rehabilitation post-injury or surgery.

Exercise Regimens for Knee Health
- Strength Training: Strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings, can help stabilize and protect the joint.
- Flexibility Exercises: Regular stretching can maintain or improve the knee’s range of motion, reducing the risk of injuries.
- Low-Impact Cardio: Activities like swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical machine can maintain fitness without putting excessive strain on the knees.
Lifestyle Modifications and Ergonomic Considerations
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the stress on knee joints.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Proper footwear, knee-friendly furniture, and workspace setups can help reduce knee strain in daily activities.
- Posture and Alignment: Proper body alignment, especially during physical activities, is crucial in preventing knee injuries.
Rehabilitation Post-Injury or Surgery
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program is essential for recovery after knee surgery or injury. It helps in restoring strength, flexibility, and function.
- Patient Education: Understanding the injury, the recovery process, and how to prevent future injuries is critical.
- Progressive Loading: Gradually increasing activity levels under supervision ensures that the knee is not overburdened during the recovery process.
Nutrition and Supplements for Knee Health
A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, plays a vital role in maintaining knee health and aiding recovery. Certain supplements can also be beneficial:
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for bone health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, they can help reduce inflammation.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: Often used to support joint health.
A proactive approach to knee health, combining exercise, lifestyle changes, and proper nutrition, can significantly reduce the risk of knee injuries and degenerative conditions. In the next section, we’ll provide a comparative analysis of different treatment modalities to give you a clearer understanding of their efficacy.
Comparative Analysis of Treatment Modalities
When it comes to treating knee pain, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The effectiveness of different treatment approaches can vary based on the individual condition, severity of the symptoms, and patient preferences. Here, we compare conventional medicine with chiropractic care, highlighting their respective efficacies.
Efficacy of Different Treatment Approaches
Conventional Medicine:
- Typically involves the use of medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery.
- Medications like NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) can effectively reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy can improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Surgical interventions are often considered for severe cases or when conservative treatments have failed.
Chiropractic Care:
- Focuses on manual therapies and mobilization techniques to improve joint function and relieve pain.
- Often used in conjunction with other therapies like exercise and lifestyle modifications.
- It can be particularly effective for certain types of knee pain, especially those related to joint mechanical problems.
Conventional Medicine vs. Chiropractic Care
- Scope: Conventional medicine offers a broad range of treatments, including pharmacological interventions and surgery, while chiropractic care focuses more on manual therapies and comprehensive approaches.
- Approach: While conventional treatments often focus on symptomatic relief, chiropractic care aims to address the underlying causes of pain.
- Outcomes: Both approaches have shown efficacy in managing knee pain, with the best outcomes often achieved through a combination of methods tailored to the individual patient.
Each treatment modality has its strengths and is often most effective when part of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to knee pain management.
Expert Insights
Incorporating insights from healthcare professionals, we find a consensus on the importance of an individualized treatment plan. Experts often recommend a combination of therapies, acknowledging that what works best for one patient may not be as effective for another.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
As we look to the future, ongoing research continues to shed light on new and improved ways of managing knee pain. Innovations in medical technology and a deeper understanding of knee pathologies promise to enhance treatment options and outcomes.
In the next section, we’ll delve into these emerging research areas and discuss potential future directions in the field of knee pain treatment.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
The field of knee pain treatment is continuously evolving, with ongoing research opening up new possibilities for more effective management and recovery. Understanding these advancements is key to anticipating the future of knee care and treatment.
Overview of Ongoing Studies
- Biological Therapies: Research is actively exploring the use of biological materials, such as stem cells and growth factors, to regenerate damaged knee tissues. These therapies have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of degenerative knee conditions.
- Customized Knee Implants: Advances in 3D printing and material science are enabling the development of customized knee implants that match the patient’s anatomy, potentially improving surgical outcomes.
- Wearable Technology: The use of sensors and wearable devices to monitor knee health and function in real-time could lead to more personalized treatment plans and improved rehabilitation strategies.
The future of knee pain treatment lies in personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual’s specific condition, genetics, and lifestyle. With these advancements, we can look forward to more effective, less invasive treatment options and quicker recovery times.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the various facets of knee pain, from its causes and diagnosis to the latest in treatment and rehabilitation approaches. The key takeaway is the importance of a personalized approach to knee pain management, one that considers each individual’s unique needs and circumstances.
As research continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and effective treatments for knee pain. However, the cornerstone of good knee health remains prevention, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle. We encourage readers to proactively manage their knee health and seek professional advice when needed.
Remember, taking care of your knees is not just about addressing pain; it’s about maintaining mobility and quality of life. So, stay informed, stay active, and don’t hesitate to seek help when you need it.
References:
Knee Pain: The Self-Help Guide by Garrett, John, Reznik, Bob, Steadman, Dick.
- This guide provides insights into self-help strategies for managing knee pain, including exercise and fitness tips.
The Knee Book – A Guide to the Aging Knee by Rosen, Adam S.
- This book delves into chronic discomfort and the steps one can take to manage knee pain, particularly in aging knees.
The Knee and Shoulder Handbook: The Keys to a Pain-Free, Active Life
- Filled with practical advice and colour photographs, this book educates on how to improve and safeguard orthopedic health, with a focus on the knee and shoulder.
A Case-Based Approach to Knee Pain by Peter Murphy
- An evidence-based, user-friendly review of common knee pathologies, this book is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals.
The Knee: Pain Medicine: A Case-Based Learning Series
- It offers a case-based approach to diagnosing and managing common knee problems, making it a useful resource for understanding knee pain.



0 Comments